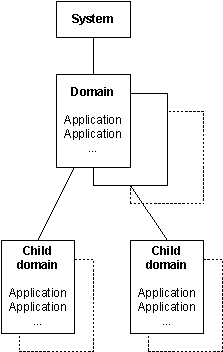
Domain
A domain is associated with one or more applications, typically the applications that take part in, or are associated with those activities.
Domains classify applications by their power requirements and dependencies. A domain is defined as a type of activity, or a class of system services, for example, telephony, networking, or camera. The exact definition depends on the device.
A domain is associated with one or more applications, typically the applications that take part in, or are associated with those activities. Applications register with a domain, and are then said to belong to that domain. Domain population by applications is a dynamic process, as applications can also leave a domain.
A domain has a power state, i.e. Active, Standby or Off. The power state is updated by the domain manager through the publish & subscribe mechanism. After registration with a domain, applications typically maintain an outstanding request to be notified of changes to the domain's power state.
Domains form a tree structure, with parent-child relationships. The architecture permits power transitions to apply to specified domains either as a result of user action, or by individual application request, or by the device's power management policy. The domain tree defines the order in which power transitions occur.
For transitions to the Off or Standby state, all applications within a domain are notified of the transition; the transition is considered complete for a domain when all of its applications have acknowledged the transition (and completed whatever action they deem necessary to save their state). Notification proceeds from child domains up to the parent domain. A domain transition can only start when all of its child domains have successfully completed their power state transition.
For transitions to the Active state, notification happens in the reverse order, starting with the parent domains and proceeding down the tree to the child domains.
Domains are identified by a domain Id. This is an 8-bit wide number and is defined as being of type TDmDomainId. The Symbian platform defines two generic domain Ids: KDmIdApps and KDmIdUiApps in domaindefs.h. However, the Domain Management Policy DLL can define additional policy-specific domain identifiers.
Copyright ©2010 Nokia Corporation and/or its subsidiary(-ies).
All rights
reserved. Unless otherwise stated, these materials are provided under the terms of the Eclipse Public License
v1.0.