Setting Microsoft OS Descriptor
This section describes how to set the Microsoft OS Descriptor (MOD) for using Symbian MTP over USB services.
Before you start, you must:
Have a general understanding of the MTP Enhanced Specification v0.95.
Have a general understanding of the USB 2.0 Specification (particularly Chapter 9.3 which describes the request types).
Understand Microsoft-Defined USB Descriptors, Microsoft OS Descriptors and Extended Compat ID OS Feature Descriptor Specification in detail.
Understand the Symbian MTP over USB architecture.
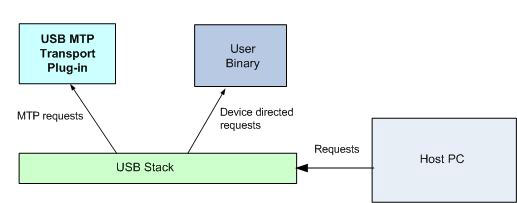
The USB Device Working Group does not define the class and sub-class ID for MTP. To allow a Symbian device to plug into Windows and handle MTP requests without installing software or requiring user interactions, device creators must provide Microsoft OS Descriptor (MOD) support in their user implementations.
Two MODs must be supplied by the Symbian device: The OS string descriptor which stores vendor-specific information and the OS feature descriptor which contains the compatible ID (compat ID) and MTP sub-compatible ID (sub-compat ID). The compat ID is the class code for MTP. After getting a valid OS string descriptor, Windows will try to get the compat ID for MTP. The driver or class for MTP is finally loaded on Windows to handle MTP requests.
To enable Symbian MTP over USB, device creators must implement a MOD solution. The implementation is referred to as user implementation. The implementation can be built into a user binary such as EXE or DLL. The user binary must be started up or loaded any time before enabling the MTP over USB.
The following tasks must be completed in the user implementation:
Load the USB Logical Device Driver (LDD) and open an LDD client.
After the user binary is loaded, the LDD must be loaded and the LDD client must be opened. The string OS descriptor can then be written into the LDD in the next step.
Set the OS string descriptor to the LDD.
A USB device which supports MOD must contain an OS string descriptor. Windows sends a request to the device to retrieve the OS string descriptor from the LDD.
Route device-directed requests to the user binary.
In the next step, Windows will send a control request to the device to get the compat ID OS feature descriptor. This request is vendor-specific and device-directed and must be handled by device creators in their user implementation. To enable the USB Stack to route the request to the user binary, the user implementation must call RDevUsbcClient::SetDeviceControl(). Device-directed requests from the PC are all then routed to this instance of RDevUsbcClient.
Provide an OS feature descriptor handler.
Once a valid OS string descriptor is returned, Windows sends another control request to get the Microsoft extended compat ID OS feature descriptor.
Once the compat ID has been returned to the PC it can load the right MTP driver and class to handle MTP requests.
Note: The string OS descriptor is written into the LDD. The OS feature descriptor is returned by the user implementation at runtime.
For more information about device directed requests and other types of requests, refer to USB 2.0 Specification Chapter 9.3. For more information about the OS string descriptor and OS feature descriptor, refer to Microsoft OS Descriptors.
Copyright ©2010 Nokia Corporation and/or its subsidiary(-ies).
All rights
reserved. Unless otherwise stated, these materials are provided under the terms of the Eclipse Public License
v1.0.