Dynamic Behaviour
Describes the dynamic behaviour of the Digitizer Driver. The description shows the use of the template port.
The design assumes that interrupts are generated by pen-down events; however, there is no difficulty in adjusting your implementation to deal with interrupts generated by pen-up events.
The heart of the design is a DFC that reads digitizer data samples when the pen goes down, and then samples the digitizer at regular intervals until the pen goes up. These samples are accumulated in a buffer in the platform independent layer. When enough samples have been gathered, the platform independent layer averages them, processes them, and issues pen movement events.
In the template port, the behaviour of the platform specific layer is based on three states: |
The template port represents these three states using the enum values of the enum TSate, defined within the scope of the DTemplateDigitiser class (derived from DDigitiser). The enum values are: |
"power up" |
E_HW_PowerUp |
"collect sample" |
E_HW_CollectSample |
"pen up debounce" |
E_HW_PenUpDebounce |
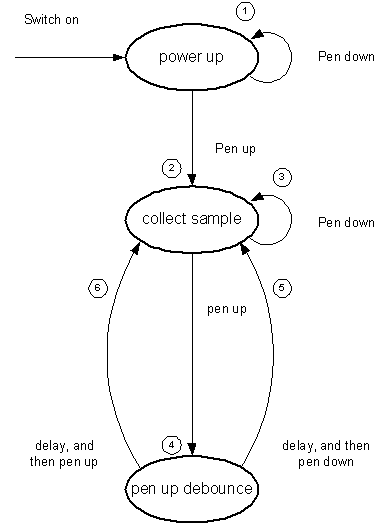
State diagram
The flow of control through the digitizer is described by this state diagram. The notes following relate to this state diagram on the left-hand side.
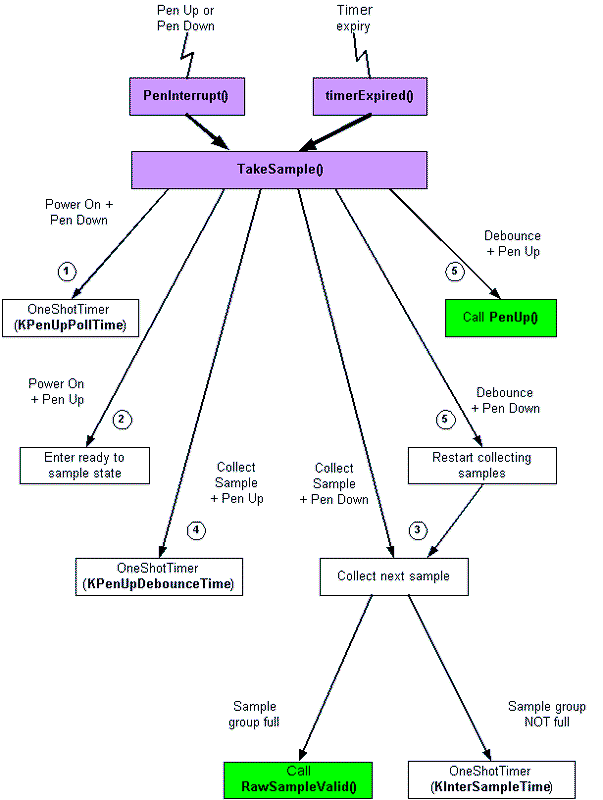
The diagram on the right-hand side shows, in a simplified form, the flow of control. The numbers correspond to the state diagram numbers. Calls into the platform independent layer are shown in green boxes; important functions are shown in purple boxes.
If the pen is down at power on, i.e. when in the power up state, the device keeps sampling the digitiser at regular intervals until the pen is up. In the template port, the interval is defined by the constant KPenUpPollTime
If the pen is up at power on, i.e. when in the power up state, or when the pen is first lifted, the sampling is initialised; see Step 6 - initialise sampling
If the pen is down in the collect sample state, then the digitiser coordinates are sampled at regular intervals, and stored in a buffer allocated by the platform independent layer. When a group of samples has been taken, the platform specific layer calls DDigitiser::RawSampleValid() in the platform independent layer to start the processing of the samples.
In the template port, the interval is defined by the constant KInterSampleTime; see Step 7 - take sample readings.
If the pen is lifted while in the collect sample state, then the state changes to the pen up debounce state. This state describes the situation where a pen is lifted from the device and there is uncertainty as to whether this represents a positive move by the user, or whether the pen pressure has just been reduced momentarily. A delay is scheduled to decide to see which is case is true. At the end of the interval the state of the pen is checked again. If the pen is found to be down at the end of this interval, then the state changes back to the collect sample state, and the sample buffer is reset.
In the template port, the delay interval is defined by the constant KPenUpDebounceTime.
If the pen is found to be down at the end of this interval, then the state changes back to the collect sample state, and the sample buffer is reset.
If the pen is found to be still up at the end of this interval, then the pen is assumed to be intentionally up. The sample buffer is reset in preparation for future readings, and the platform independent layer is notified that the pen is now up by calling DDigitiser::PenUp().
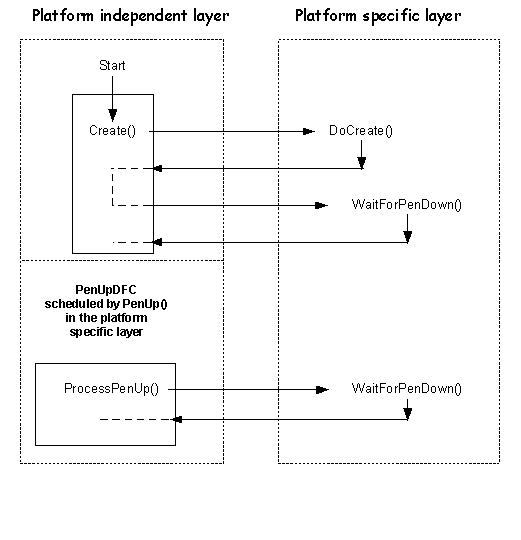
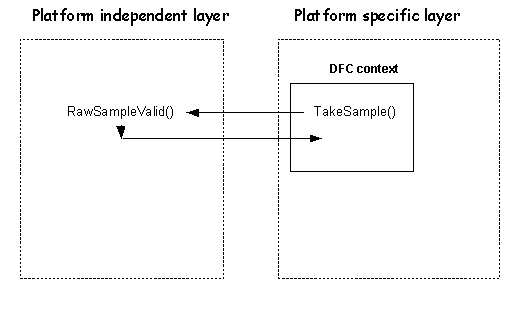
Interaction between the two layers
This section shows the main interactions between the two layers:
1
When the device is started, the platform independent layer calls the function DoCreate(). This is where the power handler should be registered, interrupts bound and any other initialisation should take place.
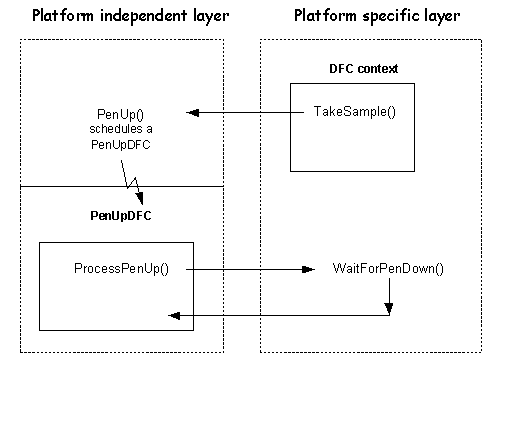
The platform independent layer then calls the function WaitForPenDown(). This is declared as pure virtual in the DDigitiser class and is implemented in the platform specific layer. This function is also called from the ProcessPenUp() function that runs in a DFC thread scheduled to run when the pen is lifted. This DFC is scheduled in the platform specific layer.
See also Step 4 - implement DDigitiser::WaitForPenDown().
2
The platform specific layer calls RawSampleValid() when it has a group of digitizer coordinates ready to be processed by the platform independent layer. This is called in the context of a DFC thread, the DFC being queued when the digitizer interrupt is fired.
3
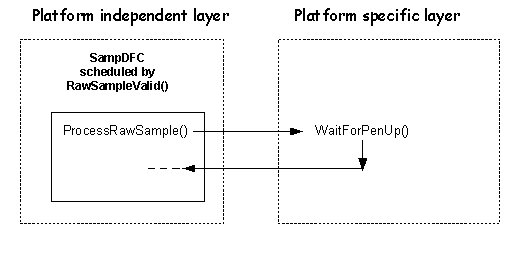
The platform independent layer calls WaitForPenUp() to request another sample from the hardware. This is declared as pure virtual in the DDigitiser class and is implemented in the platform specific layer. The function is called after the platform independent layer has processed a group of raw samples while the pen is down, and also tells the platform specific layer that the buffers in the platform independent layer can be re-used.
4
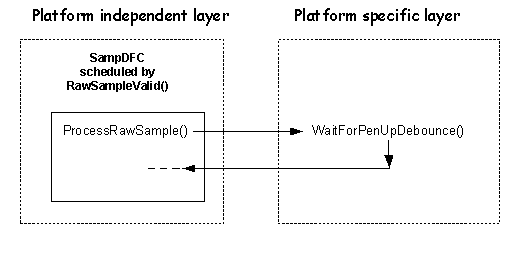
The platform independent layer calls WaitForPenUpDebounce() if a group of collected samples is not good enough. This is declared as pure virtual in the DDigitiser class and is implemented in the platform specific layer. The function is called after the platform independent layer has processed a group of raw samples while the pen is down and also tells the platform specific layer that the buffers in the platform independent layer can be re-used.
5
When the pen is lifted, the platform specific layer calls PenUp() in the platform independent layer, which then changes its internal state, issues a pen up event to the device, and then calls WaitForPenDown() in the platform specific layer.
6
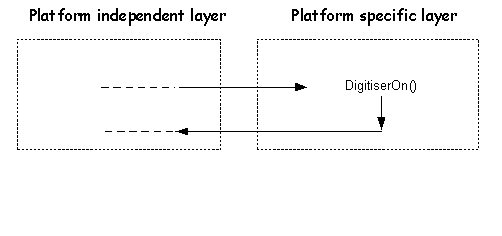
The platform independent layer calls DigitiserOn() when the device is turned on, or it may be called from the HAL. The function, implemented in the platform specific layer, and turns the hardware on if it is not already on. See also Step 3 - implement power on behaviour.
7
DigitiserOff() turns the digitizer off, and may be called as a result of a power transition, or it may be called from the HAL. If it is called from the Power Manager, the digitizer may already be off if the platform is in silent running mode. See also Step 10 - implement DDigitiser::DigitiserOff().
8
There are two functions: DigitiserToScreen() and ScreenToDigitiser() that convert digitizer coordinates to and from screen coordinates. Both are declared as pure virtual in the DDigitiser class and need to be implemented in the platform specific layer.
9
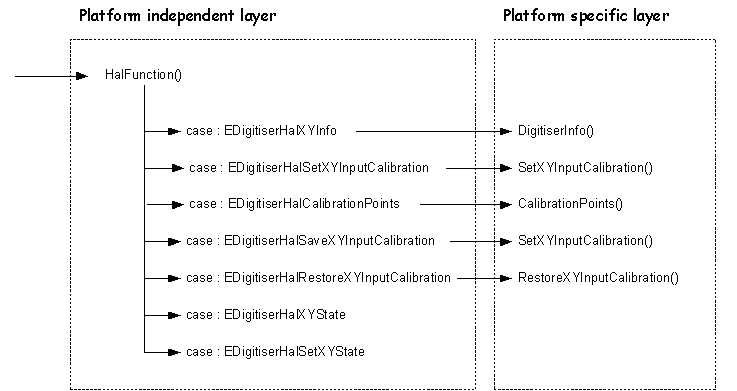
The platform independent layer provides the HAL handler for the EHalGroupDigitiser HAL groups and function-ids. This is DDigitiser::HalFunction(). It delegates the handling of 5 of the individual behaviours, as represented by the TDigitiserHalFunction function-ids, to the following functions, declared as pure virtual in the DDigitiser class, and implemented by the platform specific layer:
Copyright ©2010 Nokia Corporation and/or its subsidiary(-ies).
All rights
reserved. Unless otherwise stated, these materials are provided under the terms of the Eclipse Public License
v1.0.