Policy Evaluator Plug-in
This section explains the user prompting function in the Messaging Middleware module. It also explains how to extract the serial buffer from the various Message Type Modules (MTM) of messaging components to the User Prompt Service (UPS) Policy Evaluator plug-in.
Overview
The Messaging Middleware module enables the users to automatically request the user's permission for sending messages. The user's permission for outbound messages depends on the capability of the client application that sends the email or SMS message. The phone users are prompted to decide if any activity that can be billed (for example, sending an email message or an SMS message) must be allowed or not. The phone user is prompted with a dialog box to allow or deny the operation, and to choose if that decision should apply to one operation, or always for a particular client application.
If the client application uses the SendAs server to send email or SMS messages, then the user is prompted at the SendAs server stage only and not at the server MTM stage. This behaviour can be configured at ROM build time.
Configuration
At ROM build time, the phone manufacturers can configure the following:
The scope of the permission granted to send email or SMS messages; that is, for one operation only or always for a particular client application.
Whether the user is prompted for processes that have the network services capability, or not.
Whether the user is prompted for processes that do not have the network services capability, or not.
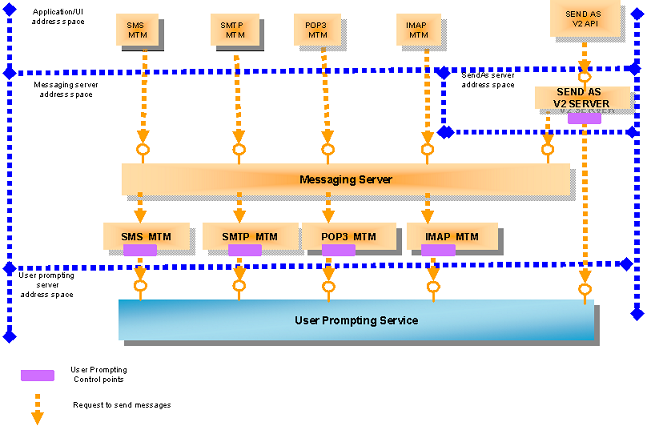
Architecture
The request to send email or SMS messages from a UI application and SendAs servers is passed from a client MTM to the Message Server, on to the corresponding server MTM, and then to UPS.
UPS uses the Policy Evaluator plug-in, which allows a security decision to be specific to an individual UI application. The Policy Evaluator plug-in prompts the phone user (using the Dialog creator plug-in) for permission to send a message, if the client application does not have the correct capability set.
- UPS
User Prompt Service
UPS allows device creators to specify whether requests made by applications to access services, such as, a request to make a telephone call, are processed silently, or whether the user is required to confirm the request. For more information on UPS, see User Prompt Service overview.
- SendAs server
The following are some of the important SendAs server features:
Send a message after the capability policing of the client application has been completed.
For more information on capability policing, see the Platform Security guide.
Allow client applications to launch an editor for a specified message type.
Allow client applications to query the message type.
For more information on SendAs server, see SendAs.
- Policy Evaluator
Policy Evaluator is an ECOM plug-in, which is responsible for generating fingerprints used to locate previous decision records related to the request. A default Policy Evaluator is provided by the Symbian platform, but device creators can also write a Policy Evaluator. For more information on Policy Evaluator, see Writing a UPS Policy Evaluators.
- Dialog creator
Dialog creator is an ECOM plug-in, which generates and displays dialog prompts. Device creators define the Dialog creator plug-in. For more information on Dialog creator, see Writing a UPS Dialog Creator.
Implementation consideration
The device creator must implement the Policy Evaluator and Dialog creator plug-ins to get the full functionality of the UPS service.
The Policy Evaluator plug-in can use the destination parameter to check if a particular request made by a client application is permissible for a particular destination.
Message Server that interact with the UPS service can pass the destination parameter (phone number, server address, and so on.) as a TDesC descriptor. If there is more than one parameter, the Message Server serialises the list of addresses to a TDesC descriptor.
To enable the device creator to use this data, the Policy Evaluator plug-in must convert TDesC to an address list.
Extracting the serial buffer
The following code snippet shows how to convert the TDesC8 descriptor to the address list. When the CPromptRequest::Destination() method is called, it returns a const TDesC reference, which contains the externalized destination values.
In order to internalize this TDesC, the plug-in needs to implement the Internalise() functionality using the following method:
void InternaliseDestinationParameterL () { const TDesC& d = iRequest->Destination(); // iRequest is a pointer of type CPromptRequest TPtrC8 p(reinterpret_cast<const TUint8*>(d.Ptr()), d.Length() * 2); RDesReadStream readStream(p); InternalizeL(readStream); } InternalizeL (RReadStream& aStream) { TInt count = aStream.ReadInt32L (); RArray<TPtrC> destinationArray; TBuf<1000 > destination ; // 1000 since this is the maximum length if the header info of a mail for(TInt I=0;i< count;++I) { aStream >> destination; destinationArray.Append(destination); } }
The device creator can now use the extracted serial buffer for displaying dialog prompts.
Copyright ©2010 Nokia Corporation and/or its subsidiary(-ies).
All rights
reserved. Unless otherwise stated, these materials are provided under the terms of the Eclipse Public License
v1.0.