SMIL Parser Overview
The SMIL Parser component uses XML DOM to validate SMIL (Synchronized Multimedia Integration Language) documents for rendering MMS (Multimedia Message Service) messages.
Purpose
Its primary purpose is to provide SMIL parsing and composing functionality for MMS. However, the component has also been designed to provide support for parsing and composing other types of XML document, for example XHTML.
Architecture
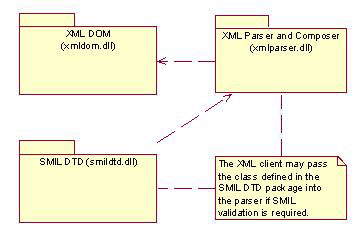
The SMIL Parser component comprises of the following elements:
A generic set of classes that can represent the contents of an XML file in an object hierarchy for efficient processing. These classes are referred to as the Mini-DOM, because they use some but not all concepts from the DOM (Document Object Model). The classes can perform syntax checking and validation with regard to a specific DTD set at run time.
An interface class that defines the signature for the necessary DTD validation functions. Any DTD-specific validation class is derived from this, and provides an implementation of these functions.
A parser that can read an XML file and can generate Mini-DOM objects.
A composer that can take a Mini-DOM object tree and output an XML file.
The following sections gives detailed explanation of the above elements:
XML Mini-DOM
The XML Mini-DOM classes are based on a subset of the DOM classes. The Mini-DOM is a subset, because it is not intended to support some of the more ambitious or obscure uses of XML. It also discards some of the theoretical layers. For example, attributes are not created as separate nodes, but are member data of element objects. The Mini-DOM is not intended as a porting API whereby applications written on other platforms using the DOM can be trivially ported to the Symbian platform.
When an XML file is parsed, and a Mini-DOM tree is created, the Mini-DOM classes provide an API to navigate through the document objects and to query the element attributes. When an XML file is to be composed, the Mini-DOM provides an API to inquiry the elements allowing the XML Composer to produce a textual representation.
SMIL DTD
SMIL DTD allows a Mini-DOM tree to be validated for a specific DTD. A DTD interface class MXMLDtd is defined from which specific DTD classes are derived. The Mini-DOM can then call DTD-specific functions through implementations of the interface.
XML Parser
XML Parser is a single-pass parser with a two-stage pipeline. The first stage is basic lexical analysis that reads the data from a source, performs some housekeeping and normalization functions on it, and passes on meaningful sections of text to the second stage for parsing.
The following operations are performed on the input in the lexical analysis stage:
The following are the meaningful sections of text:
Complete tag definitions (for example, start tag, end tag or combined tag)
Sections of text of specific CDATA sections
The second stage is to parse elements by breaking out the element name and sequence of attribute values and creating generic attributes.
Built-in character entities are replaced by their values if they have previously been defined. Any entity references that are not recognized are left untouched.
The second parser stage creates DOM objects in a tree structure by adding new elements onto the child element list of each element. Encountering a start tag causes an element to be created under the then-current element, while encountering an end tag causes the then-current element to move up the object tree. At the same time, the end tag is compared with the relevant element to ensure that start and end tags match. If an empty element tag is encountered, then the element is created, but the position for insertion of the next tag is not descend the object tree.
XML Parser is a generic parser and has no specific functionality to any particular DTD. Instead, validation and syntax checking is done through the Mini-DOM API.
The parser carries out the act of parsing an XML file as an active object. A single activation of the object parses the whole file.
The parser takes input from a file or a buffer. Supported character sets are UTF-8 (of which ASCII is a subset) and UTF-16. Any data not beginning with a DOM is treated as UTF-8. The data is parsed and added to a DOM based structure.
XML Composer
XML Composer takes a DOM tree and produces an XML file representing the data in that DOM tree. It performs a tree walk for each element, and using the generic element API, it accesses element details and outputs the text of the elements or the character data.
During the tree-walk, elements that are not empty result in a start tag and an end tag being output. Empty elements result in a single tag being output. Instances of characters that must be replaced by built-in entity references are also replaced.
When an XML file is parsed, and the resulting object tree passed into the composer, an output file is created. The output file may not be necessarily identical to the input file: that is, comments may be lost, and white space elements may be affected as well.
APIs
The following are the important XML DOM APIs provided by the SMIL Parser component:
| API | Description |
|---|---|
Provides access to element data including attribute name/value pairs. Attribute access is by name. For example, to get the value of the width attribute, call GetAttributeL() and the value is returned as another string. DTD element classes are not necessary. All elements are constructed from the generic element class and has the following functionality:
|
|
Provides functions to read an XML file and can generate Mini-DOM objects. |
|
It is an XML document with a reference to an MXMLDtd object. |
|
Defines the signature for the necessary DTD validation functions. DTD-specific validation class is derived from this and provides an implementation of these functions. |
|
Provides functions to store the node type and name and manages a list of child nodes. |
|
Provides functions to compose a Mini-DOM object tree and output an XML file. |
Copyright ©2010 Nokia Corporation and/or its subsidiary(-ies).
All rights
reserved. Unless otherwise stated, these materials are provided under the terms of the Eclipse Public License
v1.0.