Client/server communication
Inter Process Communication (IPC) is the basis for client/server architecture. Clients and servers run in different threads, although not necessarily in different processes, and communicate through message passing protocol. There are no direct pointers between the parties, leaving the integrity of the server and its resources untouched by clients. For more information, see Introduction to the client/server architecture .
Communication between the client and the server is managed by Inter-thread data transfer . Only the server and its clients can decode the parameters of the message. This is also a security feature, because process boundaries are separators of memory space, direct pointers to the client's data structures cannot be delivered. All data not fitting in the provided integers must be represented as a descriptor , and an address to the descriptor (or actually a TPckg object) is delivered within the message. The server then uses safe inter-thread read and write functions to access the provided descriptor.
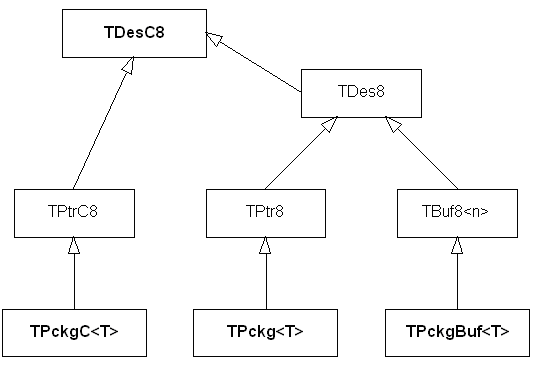
The following figure shows the relationship of the TDesC and TPckg classes.
Consider the following issues when implementing the client-side API:
-
Determine if the server is already running with the TFindServer class. If not, then it should be launched.
-
Once the server is running, create the connection with RSessionBase::CreateSession and make sure there are free message slots available to avoid lost messages.
-
When packaging message arguments, make sure they are in a format that the server understands. For more information, see TIpcArgs .
Copyright ©2010 Nokia Corporation and/or its subsidiary(-ies).
All rights
reserved. Unless otherwise stated, these materials are provided under the terms of the Eclipse Public License
v1.0.