Quick Start
Generic OS Services is a collection of components and libraries that provide generic OS level services to the Symbian platform components and applications.
Getting started with Generic OS Services
The following list briefly describes how device creators or Symbian Developers can use the APIs of the components and libraries provided by Generic OS Services:
-
Use the Plug-In Framework (ECom) APIs to register, discover plug-ins and load appropriate plug-ins.
-
Use the P.I.P.S. libraries ( libc , libm , libpthread and libdl ) to port POSIX-based applications to the Symbian platform.
-
Use the Standard C++ libraries to develop or port Standard C++ applications or libraries to the Symbian platform.
-
Use the Librt library APIs to port Librt-based applications onto the Symbian platform quickly and easily.
-
Use the EUser High Level (EUserHL) library to do better string handling, resource management, and error handling and object creation along the lines of standard C++ practices. EUserHL library provides a usability layer to hide away some of the complexities of the Symbian platform.
-
Use the Zip Compression Library APIs to perform file and stream compression and decompression.
-
Use the task scheduler APIs to develop applications with scheduling options and capabilities.
-
Use the Active Backup Client APIs to create backup and restore software with complete control of the data backed up and restored.
-
Use the HTTP Utilities library APIs to extract URI components, construct and modify Uniform Resource Indicators (URIs), text utilities, and URI component utilities required to work with URIs.
-
Use the MIME (Multipurpose Internet Mail Extension) Recognition Framework APIs to implement data type recognition using MIME recognizer plug-ins.
-
Use the Basic Application Framework Utilities library (BAFL) to in turn use utilities, such as clipboard, command-line parser, descriptor array, environment change notifier, incremental matcher, resource files, localized names of plug-ins, system sounds and string pools.
-
Use the Base Services Utility library (BSUL) to validate messages and handle errors.
-
Use the Activity Manager library to enable clients to monitor user inactivity (idle time) and user activity (key press).
-
Use the System Utility library to perform the following tasks:
Architecture
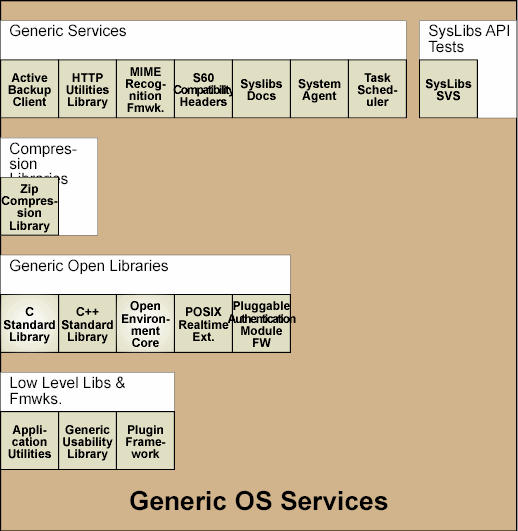
The Generic OS Services module is a group of non-related components and libraries that provide OS level services to other components of the Symbian platform. The components and libraries in Generic OS Services are grouped into the following collections:
The following diagram outlines the Generic OS Services collections and components associated with each collection:
Technologies
Generic OS services enables, implements or uses the following technologies:
-
zlib: The Zip Compression Library (EZLib) provides C++ wrapper classes that encapsulate the functionality of the Open Source zlib library v1.2.3. It provides stream and file compression and decompression functionalities.
-
Standard C++: A Standard C++ environment with IOStream and STL (Standard Template Library) libraries enables you to develop or port Standard C++ applications or libraries quickly and easily onto the Symbian platform. For more information, see the Standard C++ Porting Tutorials section.
-
P.I.P.S. Is POSIX on Symbian Platform (P.I.P.S.): P.I.P.S. provides an API layer, above the Symbian platform native APIs, that is more closely aligned with industry standard APIs making Symbian software development more accessible to Symbian Developers who program using the C language. Symbian Developers can use the P.I.P.S. libraries ( libc , libm , libpthread and libdl ) to port POSIX-based applications to the Symbian platform. For more information, see the P.I.P.S. Porting Tutorials section.
-
POSIX.1b, Real-time extensions: The Librt library enables support for POSIX.1b, Real-time extensions on the Symbian platform and is based on the Linux Standard Base (LSB) 3.1 specification. It covers features such as shared memory, clocks and real time emulation for timers. Support for the Librt library on the Symbian platform enables you to port Librt-based applications onto the Symbian platform quickly and easily. For more information, see the Librt section
-
MIME (Multipurpose Internet Mail Extension): MIME is an internet standard system for identifying the type of data in a file or stream. Types can include graphics, photos, audio, video files and formatted text. MIME type recognition enables devices to identify data in streams or files and start appropriate applications automatically.
This technology is implemented by the MIME recognition framework component. The MIME recognition framework implements data recognition using MIME recogniser plug-ins. For more information, see the MIME Recognition Framework section.
-
ECom Plug-in: The Plug-in (ECom) framework is a generic framework that enables registration and discovery of plug-ins, and the loading of an appropriate plug-in. The Plug-In framework is intended to provide a common and system-wide mechanism for instantiating a dynamically determined component. For more information, see the Plug-in Framework section.
Copyright ©2010 Nokia Corporation and/or its subsidiary(-ies).
All rights
reserved. Unless otherwise stated, these materials are provided under the terms of the Eclipse Public License
v1.0.