Dispatch Layer
This topic describes the dispatch layer of the Common TSY.
The dispatch layer is a shim between the Common TSY and the Licensee TSY. The dispatch layer is implemented by the library ctsydispatcher.dll.
The dispatch layer provides:
An interface based on the functional units of the common TSY.
Packing and unpacking of the messages between the Common TSY and the Licensee TSY
Simple input and output parameters for the Licensee TSY
Call-back functions for the Licensee TSY to send the updates and status messages to the Common TSY.
Message Manager
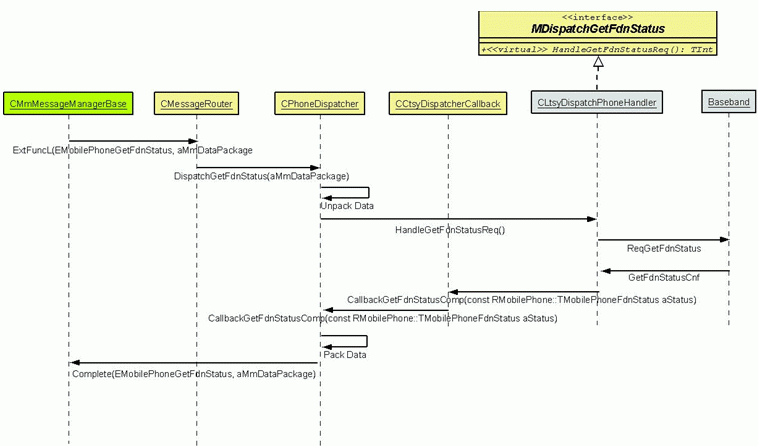
The messages from the CTSY are passed to the dispatch layer by the CMmMessageManagerBase functions.
Message Router
The message router receives the request messages from the CTSY and forwards them to the appropriate dispatcher. The dispatch layer contains many dispatcher classes based on the functional units.
Dispatcher Classes
The Common TSY with the dispatch layer decreases the time to develop a Licensee TSY. The dispatch layer contains the CMessageRouter and provides the factory class CLtsyFactoryV1. The dispatch layer also contains the dispatchers.
The main role of the dispatcher is to handle the messages between the message router and the LTSY. The factory class is responsible for creating the required handlers. The dispatcher is responsible for packing the call-back messages from the LTSY and unpacking the messages from the message router for passage to the LTSY. There is a dispatcher class for each functional unit such as SMS, Phone or Cell Broadcast. The following table describes the dispatcher class for each functional unit:
| Functional Unit | Dispatcher class name |
|---|---|
Call Control |
|
Phone |
|
Security |
|
Cell Broadcast |
|
Own Number Phonebook Store |
|
Phonebook store |
|
Emergency Number Phonebook Store |
|
SIM |
|
SMS |
|
Multiparty Call |
|
Supplementary Services |
|
Packet Data Services |
|
SIM Application Toolkit |
CCtsyDispatcherCallback class provides the methods to the LTSY to send the status and service complete messages to the CTSY.
CTSY Requests
The dispatch layer provides the interface between the CTSY and LTSY.
The telephony client requests the services from the telephony server.
The telephony applications request the telephony services like request for a voice call, data call or a fax call.
The telephony server sends the request to the CTSY.
The CTSY sends the requests to the dispatch layer.
The dispatch layer unpacks the request message and calls the methods in the LTSY to service the telephony client request.
The LTSY must implement the interfaces of the dispatch layer to accept the client requests. The implementation depends on the baseband design. If a telephony client request is not available or not implemented in the device KErrNotSupported or a similar error is returned to the clients.
The functions calls to the LTSY have a standard convention:
TInt Handle<FuncDesc><Type>(<arg list>);
TInt is the return code
FuncDec describes the function call
Type is Sync for synchronous calls or Req for asynchronous request messages.
Call-back Functions
The CCtsyDispatcherCallback class functions provide the interface for the LTSY to communicate with the dispatch layer. A pointer to this instance is passed to the LTSY. All Req type calls from the dispatch layer must be accompanied by a call-back function call. The call-back functions are called by the LTSY to notify completion of a request or to update a status. The dispatch layer packs the request messages with the data. The data contains the request command parameters from the telephony server client. An example of a request command is to dial a number.
The call-back functions have a standard name convention:
void Callback<FuncDesc><Type>(<arg list>);
FuncDesc is the description of the call-back function such as GetHomeNetwork.
Type is either Comp or Ind.
Comp is used in the call-back functions that notify a request is complete. Ind is used in the call-back functions that notify events to the CTSY. The call-back function with IND prefix are unsolicited.
Copyright ©2010 Nokia Corporation and/or its subsidiary(-ies).
All rights
reserved. Unless otherwise stated, these materials are provided under the terms of the Eclipse Public License
v1.0.