SUPL Push API
The SUPL Push API is used to process SUPL INIT messages sent from a SUPL Location Platform (SLP).
Note: From Symbian^3 the SUPL Protocol Module is deprecated. For the preferred way of using SUPL see SUPL Proxy Protocol Module.
Purpose
This document describes the SUPL Push API which is used to process SUPL INIT messages sent from a SUPL Location Platform (SLP). A SUPL INIT message is sent from an SLP to a SUPL Enabled Terminal (SET) to start a network initiated location request.
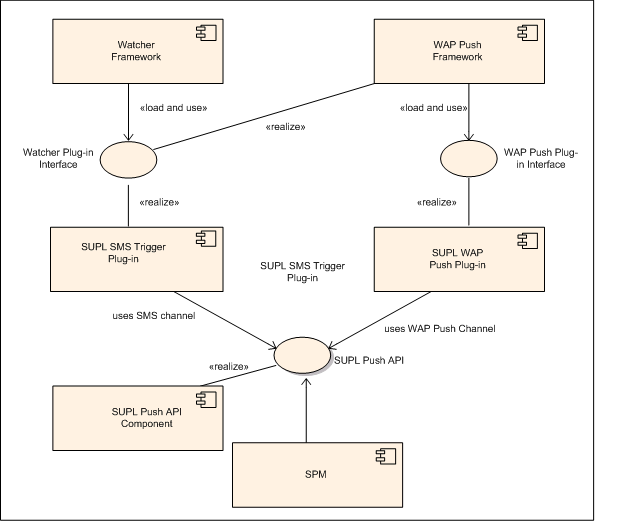
SUPL Protocol Module Overview describes how the WAP Push plug-in and test SMS Trigger plug-in use the SUPL Push API to forward SUPL INIT messages to the SUPL Protocol Module (SPM).
This document is intended for Symbian licensees who want to create their own handlers to process SUPL INIT messages. Licensees who simply want to use the WAP Push plug-in do not need to use this API.
Introduction
Secure User Plane Location (SUPL) is a standard for enabling Location Based Services using IP for most of the communication between a SET and an SLP. To start a network initiated request, the SLP must send a SUPL INIT message to a SET. The flow of events is as follows:
To start a location request, the SLP sends a SUPL INIT message to the SET using WAP Push or SMS Trigger [1].
To support SUPL, the LBS subsystem ROM is built to include the SUPL WAP Push plug-in or an SMS Trigger plug-in as described in SUPL Protocol Module Quick Start.
The SUPL INIT message is received by either the WAP Push plug-in (loaded by the WAP Push Framework) or the SMS Trigger plug-in (loaded by the Messaging Watcher Framework) shown in figure 1. Either plug-in processes a SUPL INIT message and call the methods of the SUPL Push API to cause the SUPL Protocol Module to open a socket connection to the SLP.
A licensee can also create their own SUPL INIT handler to process messages received from an SLP. All SUPL INIT handlers must use the SUPL Push API.
The SLP and the SET process the location request as described in SUPL sequence diagrams.
Symbian plug-ins that use the SUPL Push API
Symbian provides two plug-ins that can process SUPL INIT messages and call the SUPL Push API:
The SUPL WAP Push plug-in receives SUPL INIT messages sent via WAP Push.
The Symbian test SUPL SMS Trigger plug-in receives SUPL INIT messages sent via SMS.
The SUPL WAP Push handler plug-in and SUPL SMS Trigger plug-in use the SUPL Push API to notify the SUPL Protocol Module that an SLP is starting a network initiated location request.
SUPL WAP Push plug-in
The Symbian platform includes the WAP Push Framework to process WAP Push messages. If the Symbian SUPL WAP Push plug-in is installed, the WAP Push Framework uses it to process SUPL INIT messages sent by WAP Push. The plug-in calls the methods of the SUPL Push API causing the SUPL Protocol Module to open a connection to the SLP.
The SUPL WAP Push handler plug-in is a production component. Licensees can install the plug-in in their ROM so that it is available to the WAP Push Framework. Licensees do not need to develop their own WAP Push handler plug-in. See SUPL Protocol Module Quick Start for details of how to configure an LBS ROM to include the WAP Push plug-in.
Source code for the WAP Push plug-in can be found at <LBS_SOURCE_ROOT>/LbsSuplProtocolModule/SuplWapPush and consists of a single class which gets the SUPL INIT message body and uses the SUPL Push API to forward it to the SUPL Protocol Module.
SUPL SMS Trigger plug-in
If the Symbian SUPL SMS Trigger plug-in is installed, it is loaded on OS startup by the Watcher Framework, which uses it to process SUPL INIT messages sent by SMS Trigger. The plug-in calls the methods of the SUPL Push API causing the SUPL Protocol Module to open a connection to the SLP.
Source code for the SMS Trigger plug-in can be found at <LBS_SOURCE_ROOT>/LbsSuplProtocolModule/SuplSmsTrigger and consists of a single class which gets the SUPL INIT message body and uses the SUPL Push API to forward it to the SUPL Protocol Module.
SUPL Push API description
The SUPL Push API is used to notify the SUPL Protocol Module that a SUPL INIT message was received from an SLP to start a network location request.
The SUPL API has two different types of client:
Clients that receive SUPL INIT messages and send them into the LBS subsystem, such as the Symbian WAP Push plug-in. These components use the SUPL Push API sender classes.
Clients that require notification of SUPL INIT messages, such as the SUPL Protocol Module. The SUPL Protocol Module uses the SUPL Push API receiver classes to receive notification of network initiated location requests.
The SUPL Push API has publishedPartner interface access.
SUPL Push API sender classes
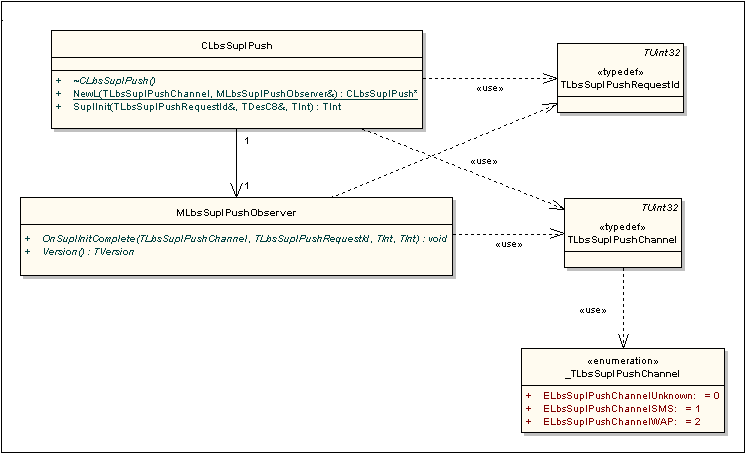
This section describes the classes of the SUPL Push API that the SUPL WAP Push handler plug-in and SUPL SMS Trigger plug-in use to send SUPL INIT messages into the LBS subsystem. Figure 2 shows the SUPL Push API sender classes. Licensees use the API sender classes to implement their own SUPL INIT handler (if required).
| Class name | Description | Header file |
|---|---|---|
The interface used to send SUPL INIT messages to the LBS subsystem. A WAP Push message handler or SMS Trigger handler creates and owns an instance of this class. The class defines the interface only and delegates all its functionality to an implementation class. |
lbssuplpush.h |
|
The observer interface used with CLbsSuplPush. The interface defines a callback method to allow message delivery results to be returned to a client. The Symbian WAP Push plug-in implements this interface to receive confirmation of SUPL INIT message delivery to the SUPL Protocol Module. |
lbssuplpush.h |
|
Defines an enumeration and a typedef for the source of the SUPL INIT message. Two 'channels' are defined: a WAP push channel and an SMS trigger channel. |
lbssuplcommon.h |
Request queueing
The SUPL Push API uses Publish and Subscribe (P&S) properties to store the details of SUPL INIT messages. Properties are written by SUPL Push API sender class clients and are read by SUPL Push API receiver class clients.
One potential problem with using P&S properties occurs in the situation where multiple calls to CLbsSuplPush::SuplInit() are made in quick succession. Without a means of queueing requests and synchronising access to P&S properties, it would be possible for property values to be overwritten without first being read, leading to the possible loss of some SUPL INIT messages.
The implementation of the SUPL Push API queues SUPL INIT messages that are sent by API clients by calling CLbsSuplPush::SuplInit() and also synchronises access to the P&S properties so that all received SUPL INIT messages are processed by the SUPL Protocol Module.
API restrictions
The SUPL Push API can be used by up to two threads, each of which must use a different 'channel' as specified by _TLbsSuplPushChannel. An API client specifies the channel it wants to use when it calls CLbsSuplPush::NewL(). Two channels are defined: ELbsSuplPushChannelWAP and ELbsSuplPushChannelSMS.
A single thread in an API client can create multiple instances of CLbsSuplPush, but each instance must use the same channel.
The Symbian WAP Push Framework instantiates multiple copies of the SUPL WAP Push plug-in to handle multiple SUPL INIT messages. All of the instances are started by the same WAP Push Framework thread.
There is only one instance of the Symbian test SUPL SMS Trigger plug-in which is loaded by the Messaging Watcher Framework and all messages are processed by the same thread.
Licensees who implement their own method of handing SUPL INIT messages without using the Symbian WAP Push Framework or the Watcher Framework must remember the API limitations:
A maximum total of two threads can use the API concurrently.
Each thread must use a different 'channel'.
SUPL Push API receiver classes
This section describes the classes of the SUPL Push API that the SUPL Protocol Module uses to receive SUPL INIT messages.
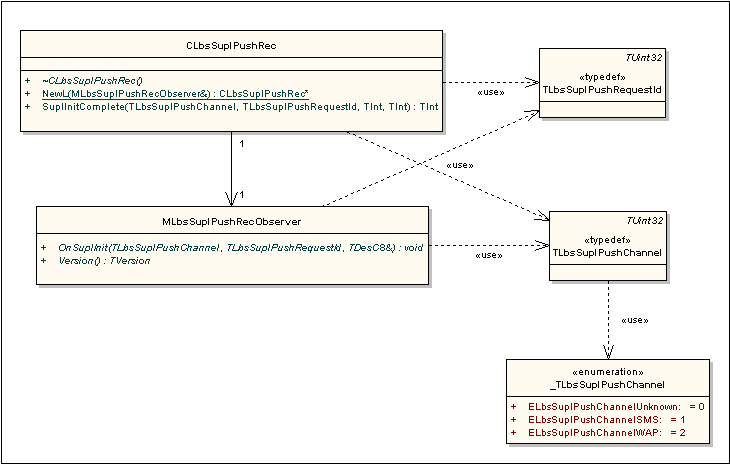
Figure 3 shows the SUPL Push API receiver classes. Symbian licensees do not need to use the receiver classes - they are used by the Symbian reference SUPL Protocol Module.
| Class name | Description | Header file |
|---|---|---|
The observer interface that the SUPL Protocol Module implements to receive SUPL INIT messages sent via CLbsSuplPush. |
lbsuplpushreceiver.h |
|
The interface defines a method SuplInitComplete() to allow the SUPL protocol module to notify LBS that a SUPL INIT message was successfully processed. |
lbssuplpushreceiver.h |
The SUPL Protocol Module implements MLbsSuplPushRecObserver to receive notification of SUPL INIT messages sent by using CLbsSuplPush::SuplInit(). It calls CLbsSuplPushRec::NewL() to register itself for notifications.
The SUPL Protocol Module calls CLbsSuplPushRec::SuplInitComplete() to send notification that a message was received successfully. The method MLbsSuplPushObserver::OnSuplInitComplete() is called to notify the sender that the message was received.
Sequence diagram
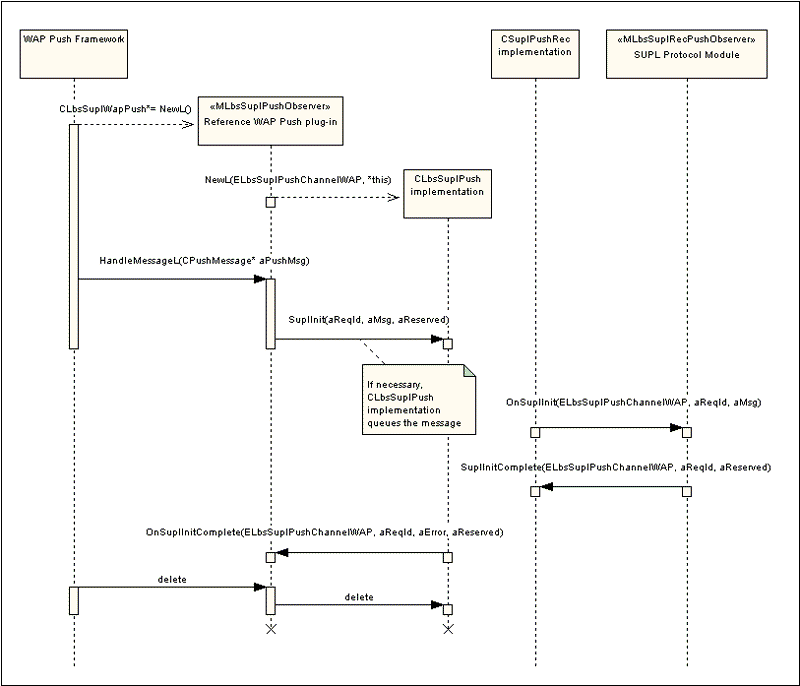
Figure 4 is a simple sequence diagram showing the WAP Push plug-in receiving a SUPL INIT message and sending it to the SUPL Protocol Module.
An SMS Trigger plug-in would use the channel ELbsSuplPushChannelSMS with CLbsSuplPush::NewL().
The error parameter aError returned in MLbsSuplPushObserver::OnSuplInitComplete() is KErrNone if the SUPL INIT was successfully processed by the SUPL Protocol Module, but may be another error code as decribed in the API reference documentation.
Note that the SUPL Protocol Module calls CSuplPushRec::SuplInitComplete() when the SUPL INIT message is received, but this does not guarantee that the network initiated location request will complete successfully.
References
[1] Open Mobile Alliance Secure User Plane Location (SUPL) Architecture OMA-AD-SUPL-V1_0-20070615-A
Copyright ©2010 Nokia Corporation and/or its subsidiary(-ies).
All rights
reserved. Unless otherwise stated, these materials are provided under the terms of the Eclipse Public License
v1.0.